Abstract
The use of textiles began when human beings felt the need to cover their bodies to protect themselves from adverse environments. Now not only clothing but also textiles are being applied in various technological sectors. We all know about aerospace technology, because of human talent and hard work we have been able to conquer space today. The role of aero-technology as well as the modern & technical textiles sectors are the main reasons behind the success of the space missions. Aerospace textile is one of the technological textiles, the production and use of textiles in space technology has increased day by day. The combination of textile technology and aeronautical technology has created a new field known as Aerospace textiles.
Keywords: Aerospace textiles, Technical textiles, Space textiles, Space suit, Aircraft textiles, High performance fibers, Textiles in space technology, Aerospace technology, G-suit.

Classification of Aerospace Textiles
These days, the design, manufacturing and application of textile composites in aerospace technology have become a very important and challenging industry. Aerospace textiles can be divided into two main types-
- Aircraft Textiles.
- Space Textiles.
1. Aircraft/Spacecraft Textiles:
The textile materials used in aircraft or spacecraft are known as aircraft textiles. Such as: floor carpet, seat cover, body part, headset, wall cover, aircraft interior designing, parachutes etc. These products are made by some high-performance fibers and manufactured fibers.
2. Space Textiles:
Apart from aircraft applications, textile fibers are used in the manufacture of spacesuits. Various raw materials are used for tailoring the spacesuit, G-suit, including fabrics made from different synthetic fibers. For example, the inner layer of the space suit is made up of nylon tricot, the middle layer is manufactured with spandex, which gives the elasticity in the space suit and the outer layer is made with urethane coated nylon.
Some Important Features of Aerospace Textiles
- Good fatigue and stress resistant
- Resistant to chemical and organic solvents
- Heat insulation and heat resistant
- Fire retardant
- High specific modulus and strength
- Good dimensional stability and comfortability
- Resistant to harmful radiation
- Light weight and flexible in handling
- Abrasive and tear resistant
- Moisture resistant
- Should be comfortable and washable
Raw Materials Used in Aerospace Textiles
High performance fibers & nanotechnical fibers and smart technology are widely used in the production of this special type of textiles such as: Polyester, Nylon tricot, Urethane – coated Nylon, Dacron, Kevlar, Carbon, Glass, Aramid, Nomex, Spandex, Spectra, Silk etc.
Carbon Fiber:
It is a very thin fibrous material with a diameter of about 0.0002 – 0.0004 inch and contains a large amount of carbon atoms because it is produced as a by-product during the cracking process of crude oil. It is also called graphite fiber. Carbon fiber is known for its high specific strength in the aerospace industry. Some basic properties are-
- Highly tensile strength.
- Heat resistant
- Do not attacked by chemicals.
Aramid/Kevlar Fiber:
Aramid fibers are manufactured from the condensation reaction of paraphenylenediamine and terephthaloyl chloride. It is highly used in space textiles industry. Kevlar is the trade name of Aramid Fiber. Some of the special features of this fiber are: Heat resistant, High specific strength, high modulus, abrasion resistant, Flexibility, High temperature, non-flammable and low brittleness of the fabric. Such fibers are particularly known for their quality and consistent delivery efficiency, which is important for aerospace and aeronautical products.
You may also like: Kevlar: A Fiber has changed the War Industry
E-Glass Fiber:
Glass fiber is the most common reinforcement material used in the aerospace industry. The density of glass fiber is higher than carbon fiber and stronger than any other inorganic fibers. E-glass was originally made for electrical wiring. Later it was noticed to have great fiber formation ability and it is commonly known as glass fiber. Which is used exclusively to make any object more powerful. E-glass is also called borosilicate fiber. Important properties of e-glass fibers are given below.
- High tensile strength
- High heat resistance
- High dimensional stability
- Fire resistance and good thermal conductivity
- Good chemical resistance
- Corrosion resistance
Alumina-boria-silica Fiber:
Nextel is the trade name for Alumina-boria-silica fiber. The strength of this fiber remains unchanged. Demonstrates flexibility even when slightly compressed at temperatures up to 1100oC.
Silicon Carbide Fiber:
This type of fiber is very similar to carbon fiber.
- Heat resistance.
- Elasticity
- Corrosion resistance
- Withstand temperatures up to about 15000C.
Nylon Fiber:
Nylon 6: 6 fiber is made from hexamethylene di-amine and adipic acid. Some basic features of nylon are heat resistance, abrasion resistant etc. The melting point of the fiber is 258oC.
Graphene:
Graphene is an important material for the aerospace technology. It consists of a single atom thick sheet and an allocation of carbons. Some recent applications include graphene coating as multifunctional material for spacecraft and aircraft structures, electrically conductive epoxy resins, and aviation electronics.
Some Important Applications of Aerospace Textiles
- Space Suit
- G-Suite
- Parachutes and Balloons
- Floor carpet
- Seat cover & Seat belt
- Body parts & Wings
- Head set
- Wall cover & Curtains
- Space Shuttle Upholstery
- Aircraft Upholstery
- Technical Fabrics
- Fiber Reinforced Composites
- Fuel Tanks & Rotor Blades
- Airbag, etc.
Space Suit
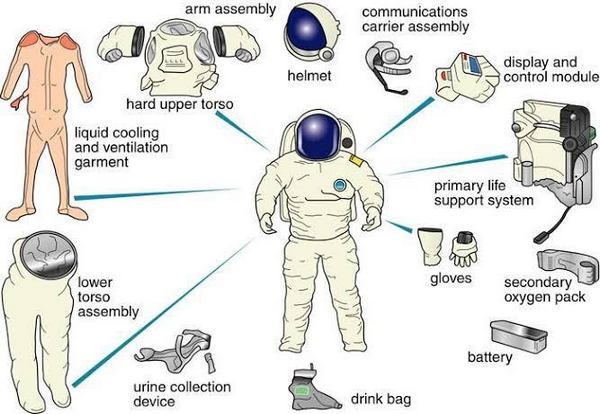
In practical terms, spacesuit is not just a set of garments, it is also called a “One Person Spacecraft”. The official name of the spacesuit is “Extravehicular Mobility Unit-EMU”. An astronaut should wearing a totally prepared, well-equipped and defects free spacesuit, as a result the astronaut can come out of the spacecraft and control himself. Must need a Spacesuit for landing on new planets. Generally, a spacesuit or EMU is a special arrangement of a set of protective clothing and equipment, which ensures the astronaut’s safe position, navigation and survival in the hostile environment inside and outside the spacecraft.
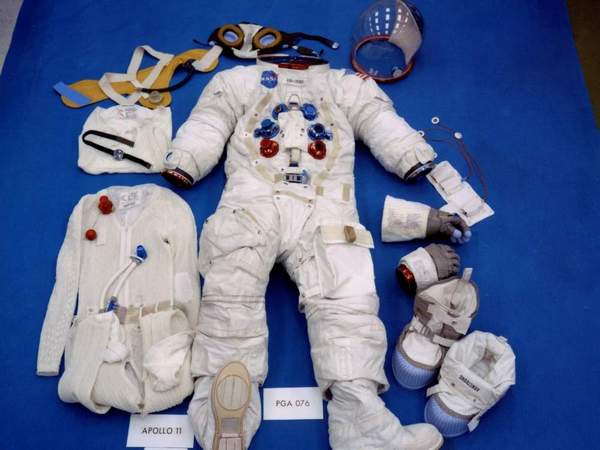

Structure and Functions of the Various Parts of Spacesuit
- Communication Carrier Assembly (CCA)
- Liquid Cooling & Ventilation Garment (LCVG)
- Maximum Absorbency Garment (MAG)
- Helmet & Extravehicular Visor Assembly (HEVA)
- Hard Upper Torso with Arm Assembly (HUT)
- Display and Control Module (DCM)
- Arm & Glove Assembly
- Lower Torso Assembly
- Portable Life Support System (PLSS)
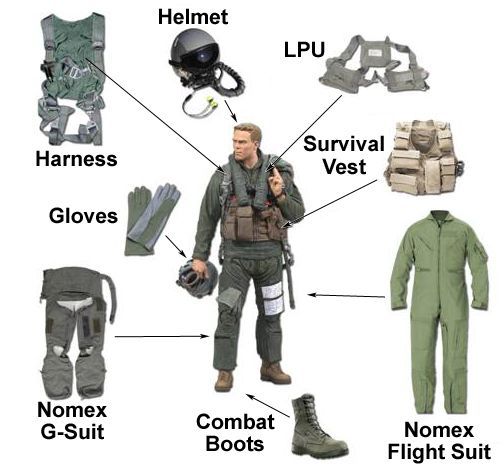
G-Suit
G-suit is a special of flight suit, it is worn by aviators, astronauts or fighter pilot in aircraft who are subjected to high gravitational acceleration force. G-suit is produced by different parts or elements like Helmet, LPU, Survival vest, Nomex flight suit, Combat boots, Nomex G-suit, Gloves etc. G-suit is containing air or liquids than can be maintained/controlled the high pressure and balancing the body parts of astronauts or aviators using a g-sensitive valve. It is a one kind of smart textiles for aerospace industry.

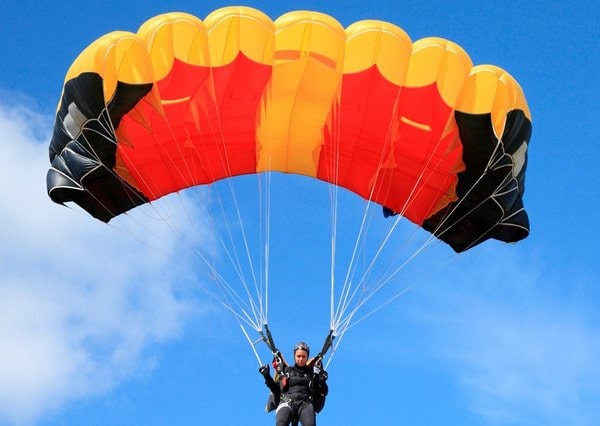
Parachutes
Parachutes are also a part of aerospace textiles. Parachute is kept as protection material for the pilots, aviators and passengers of the aircraft. Parachutes are made from different types of high-performance fibers such as Nylon, Polyester, Kevlar, Nomex etc. There are different types of parachute like Round, Cruciform, Annular, Rogallo wing, Ribbon and Ring, Ram air etc. Some important characteristics are UV, Heat and Abrasion resistant, Water proof, High specific strength and light weight.

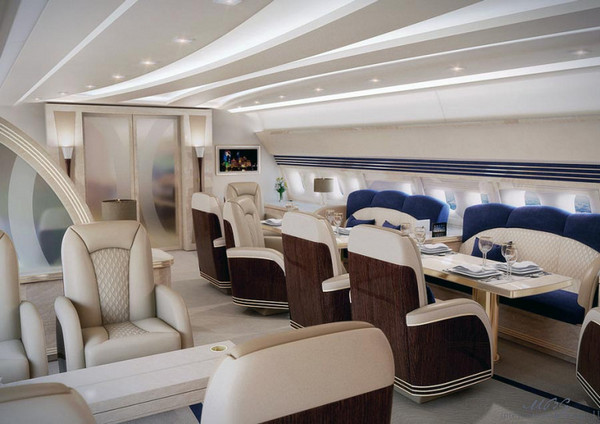
Aircraft / Spacecraft Interior Designing
Inside the spacecraft and aircraft, various textile composites are used for interior designing. From furnishing textiles to wall covering, floor carpet, seat & seat belts, curtains and other interior designs are made of textile composites. Leading technologies such as micro & nano fibers, high-performance fibers, polymers etc. have revolutionized the application of textiles in the interior design of the aircrafts/spacecrafts.

Future Developments of Aerospace Textiles
The space suit performs multiple functional tasks, providing protection to astronauts in spacecraft and space. However, the modern space suit is not advanced enough yet. NASA is preparing the Futuristic Z-2 Spacesuit of Z-2 prototype for the next generations. The weather at Mars is extremely unfavorable which is the biggest challenge in making space suits. No specimens have yet returned to Earth from Mars. In that case, the space suit engineers are thinking that the space suit made by NASA should not be affected by the environment of Mars.
Aerospace Textiles Manufacturers
- Boeing, United States
- Airbus
- Lockheed Mastin, United States
- United Technologist, United States
- Raytheon, United States
First Female Astronaut (Textile Worker)
There are very few people who have never heard of “Valentina Tereshkova.” She was the first young female astronaut. Ever since she was a child, his dream was to be an astronaut, always thinking that one day she would become a pilot and jump down from a plane with a parachute. From that dream she will be able to travel in space, having spent three days in space and orbiting the earth 48 times. Surprisingly, she was a textile worker. Valentina Tereshkova is now 88 years old. The dream of this brave woman has not been fulfilled yet. Dreaming of conquering Mars anew. NASA wants to send people to Mars in the thirties of this century. Knowing that astronauts will never return to earth, Tereshkova recently expressed a desire to be part of that mission.

Conclusion
Textiles have always played an important role in aerospace industry. May be, it is because of smart textiles technology that people have been able to conquer space now. It is possible to improve the functional properties of space textiles through further research. And may be one day we will conquer the Mars through the use of new technology with textiles. Space textiles is an important part in fulfilling that dream.
References:
- Roshan Paul “High Performance Technical Textiles” This edition first published 2019.
- Richard Horrocks, Subhash C. Anand “Handbook of Technical Textiles” Volume 1: Technical Textile Processes, Second Edition.
- Textiles in Aerospace Applications by Dr. Faheem Uddin, Textile Department, School of Science of Technology, University of Management and Technology.
- https://textilelearner.net/aerospace-textiles-raw-materials-and-applications/ Accessed date: 09/03/21
- https://www.textileblog.com/textile-application-in-aerospace-industry/ Accessed date: 09/03/21
- https://textilefocus.com/application-of-textiles-in-aerospace-engineering/ | Accessed date: 09/03/21
- https://www.slideshare.net/vigneshdhanabalan/textiles-in-aircraft | Accessed date: 07/03/21
- https://indiantextilejournal.com/articles/FAdetails.asp?id=1958 | Accessed date: 07/03/21
Author of this Article:
Md. Imran Hossain
B.Sc. in Textile Engineering
Shahid Abdur Rab Serniabat Textile Engineering College, Barisal.
Email: mdimranhossain.te@gmail.com
You may also like:
- Textile Application in Aerospace Industry
- Application of Phase Change Materials in Smart Textile
- Application of Smart Textiles in Medical and Healthcare
- Smart Textile Revolution: Towards a Smart Future
- Automation and Robotic in Sewing Technology
