What is Yarn Clearer?
Yarn clearer is a device which is used to remove faults (thick places, thin places, foreign matter etc.) from the yarn in order to increase the yarn quality and weaving efficiency. This device is mainly used in winding steps.

Following yarn defects are removed by yarn clearer:
- Thick and thin places
- Slab and neps
- Loose fabric
- Foreign materials
Different Types of Yarn Clearer:
There are two types of yarn clearer
- Mechanical yarn clearer
- Electronic yarn clearer
A. Mechanical yarn clearer:
Conventional manual-type winding machines are normally equipped with mechanical type clearer. Mechanical clearer basically consist of an adjustable slot through which the yarn passes. It traps only thick places that are greater than the slot setting. The device incorporates a cutting edge that breaks the yarn faults. Mechanical clearers are rarely used nowadays as they are not efficient in removing thin places and contaminants.
There are two types:
- Conventional blunt type
- Serrated blade type
B. Electronic yarn clearer:
The electronic yarn cleaner (EYC) is firmly established as yarn fault detector in all ordinary and automatic cone winding machines. Electronic yarn clearers are provided on winding machines in order to clear the objectionable faults and long faults if any in the yarn.
The electronic yarn clearer has been playing an important role in the market for the past three decades. It represents the last monitoring system in the spinning process where remaining disturbing faults can be eliminated and replaced by a “splice” instead of a knot which is objectionable in knitting and in weaving processes. It also represents a filter in which off-quality bobbins can be automatically separated from the yarn batch of good quality.
There are basically two principles:
- Capacitance type clearer
- Photo electric type clearer
1. Capacitance clearer:
The capacitance clearer system measures the mass per unit length and generates a voltage that is compared with a set reference value for the mean yarn thickness. The yarn is automatically cut and the fault is removed whenever the voltage difference exceeds a given maximum value. Capacitance type clearers are manufactured by Zellweger Uster Technologies.
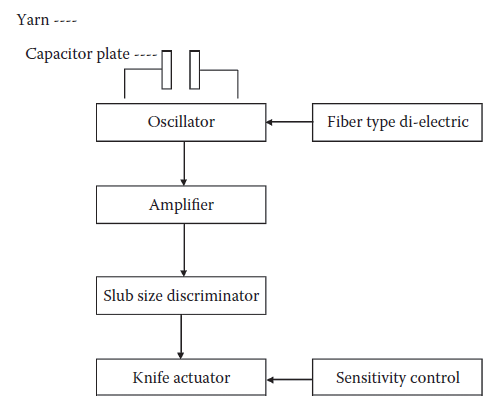
The block diagram shows the principle of the capacitance-type electronic yarn clearer. In this type, the yarn is passed through an air-spaced measuring condenser consisting of two parallel plates with air as media. The yarn fault limits according to yarn cross-section, length and spinners’ double are set by using suitable knobs on the instrument. As the yarn passes through the capacitor, according to the length and cross section of the yarn, the capacitance value is changed. This is related to the mass of the material between the plates. The condenser measures the material, and electric signals are fed to an amplifier that amplifies the signals. The amplified voltage is transferred to a discriminator that measures the preset fault limits. If the signals exceed the limits, the signal is fed forward and through a cutting impulse, and a knife is actuated to cut the yarn. A fiber type dielectric and sensitivity controls are used to get the required sensitivity during the operation (Figure 2).
2. Photoelectric clearer:
Photoelectronic yarn clearers are able to detect dark and bright foreign matter and finest transparent fibers simultaneously in raw-white as well as colored materials. In the photoelectric system, a beam is projected from a light source laterally across the yarn, and a photocell measures the intensity of the light passing by the yarn. By this way, variations in the yarn thickness can be monitored. The fault is detected and removed whenever the change in intensity is greater than a set level. Photoelectric type clearers are manufactured by Loepfe Bros. Swiss.
The block diagram shows the principle of the photo-cell type electronic yarn clearer. The yarn is passed through a light source and is scanned by the light source. Opposite to the light source, a receiver is provided to receive the light rays emitted from the light beam (Figure 3).
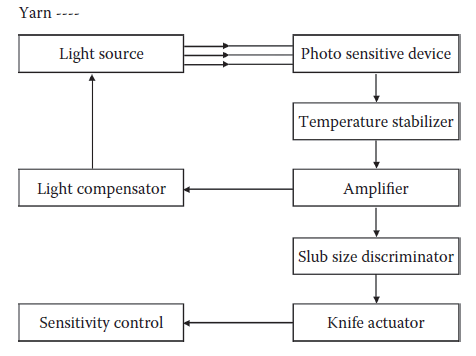
The yarn fault limits for thickness, length and spinners’ double are set by using suitable knobs in the instrument. As the yarn passes through the light source, the yarn is scanned by the light beam. The scanned portion interrupts the light beam, which changes the signal from photo-cell. These signals are fed to an amplifier that amplifies the signals. The amplified voltage is transferred to a discriminator that measures the preset fault limits. If the signals exceed the limits, the signal is fed forward and through a cutting impulse, and a knife is actuated to cut the yarn. Uster Peyer, Uster Quantum clearer, and Loepfe clearer can be used as yarn clearers.
Yarn Clearer Setting in Automatic Winding Machine:
The setting of yarn clearer is crucial in winding process in terms of quality and productivity. The various settings kept in the clearer are dependent on customer requirements. The following are the various channels available in the clearer system of the modern winding machine:
- Reference length: Length of the yarn over which the fault cross section is to be measured.
- Sensitivity: This determines the activating limit for the fault cross-sectional size.
- Yarn count: The setting of yarn count helps to provide mean value of the material being processed to which clearer compares the instantaneous signals for identifying the seriousness of faults.
- Material type: Input of fiber type being processed.
- Fault channels:
- Short thick places
- Long thick places
- Long thin places
- Neps
- Count
- Splice
- Contamination clearing: This setting removes the contaminants present in the yarn such as color thread, PP thread, jute thread, etc.
You may also like:
- What is Yarn | Types of Yarn
- Yarn Specifications and Quality Parameters
- Fancy Yarn: Types, Properties, Manufacturing Process and Application
- What is Yarn Twist | Twist Direction | Twist Level
- Yarn Count System and Determination by Different Methods
