Study on Production Strategy of Slasher Dyeing & Rope Dyeing Denim
Authors:
Md: Khairul Alam1
Md. Didar Hossain
Dept. of Textile Engineering
Daffodil International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Email: hasnat2317@gmail.com1
Supervisor:
Dr. Md. Mahbubul Haque
Professor and Head
Dept. of Textile Engineering
Daffodil International University
ABSTRACT
At first we visit some of denim fabric industries. We observed the denim production from the Warping stage to Inspection stage very carefully. We needed to commence our project work with effective analysis. In every steps of production we collect data and also analyze that. We tried to find out the difference Productivity process of both Rope dyeing and sheet dyeing denim (Warping stage to Inspection stage). We compare the Productivity process every stage with faults, wastage, production loss and actual production of Rope denim and Sheet denim. We found that the Production loss, and wastage of sheet denim is higher than the rope denim production. We also collect data from every section and work according to production procedure. For this reason we find out an acceptable result which will be perfect for effective use and will help to carry out further activities depending on the established form of work.
During our project we work carefully and effectively. The productivity process in every section along with machine specification and the major factors which are necessary to calculate productivity in every stage of production. Our efforts makes a dependable way that’s why we can easily find out our final result. The theoretical as well as the practical knowledge that we gathered from our classes and in the industry, help us to perform and complete our project with credit for this we specially convey thanks to our honorable teachers.
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Introduction:
Denim is a fabric which is more versatile more fashionable and used by global people. Though, initially the fabric was developed for using as sail cloth and also use as a cloth of gold mining laborer but at present denim is mostly used for producing garments particularly trousers for the young people Bangladesh is one of the leading producers of garments and a large share of it is denim fabric, and denim garments production which exports across the worldwide. After China Bangladesh has become the second largest denim producer. The production and exports rate are increase in Bangladesh day by day. At the processing time of denim production from warping to inspection, textile materials are carried out various pressure and stresses not only during the machine operation but also machine stoppage time or process stoppage time. If this pressure or stoppage time exceeded a given limits it will adversely affect the quality of the yarns and fabrics both physical and chemical such as shade variation elongation and also the efficiency of the machines. The main stage of manufacturing denim fabrics includes warping, dyeing & sizing and weaving. Though the weaving is same but comparatively change in other process such as warping, dyeing of manufacturing a weaver’s beam of Slasher/sheet dyeing and rope dyeing.
LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Denim:
Denim is in constant evolution and new innovations will surely influence the future of the industry. Denim is a strong cotton warp-faced textile in which the weft passes under two or more warp threads. Denims are produced by mainly twill weave. This twill weaving produces a diagonal ribbing effect. The most common denim is indigo denim, in which the warp thread is dyed, while the weft thread is undyed. Denims are produced from 4 oz. to 16 oz. / sq.yds in weight. Technically Denim is defined as a 3/1 warp faced twill but also produced from weaves like: Left hand twill, right hand twill, broken twill, cross hatches, cords, dobby’s, structures etc. Now-a-days denim has a great demand in domestic and world markets.
You may also like: History and Some Amazing Facts about Denim and Jeans
Flow Chart of Denim Production:
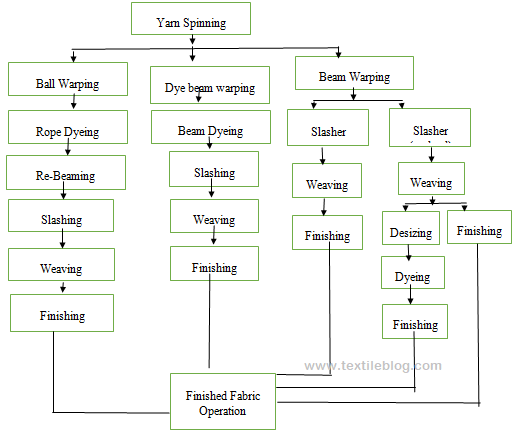
2.2 Warping:
The primary procedure in the assembling of denim is twisting. When all is said in done term, distorting is exchanging numerous yarns from a creel of single-end bundles shaping a parallel sheet of yarns wound onto a pillar or an area shaft.
Distorting is the way toward exchanging different yarns from individual yarn bundles onto a solitary bundle get together. Regularly, yarns are gathered in a sheet structure where the yarns lie parallel to one another and in a similar plane onto a bar, which is a round and hollow barrel with side spines. This is known as bar distorting.
The twist pillar that is introduced on weaving machine is known as the weaver’s bar. A weaver’s pillar can contain a few thousand finishes and for various reasons it is infrequently delivered in one task.
- Direct Warping is used for Sheet Denim production.
- Ball Warping is used for Rope Denim production
2.2.1. Direct Warping:
In direct distorting, the yarns are pulled back from the single-end yarn bundles on the creel and legitimately twisted parallel to one another on a marginally more extensive flanged shaft. Direct twisting can be utilized to legitimately deliver the weaver’s bar in a solitary activity. This is appropriate for solid yarns that don’t require estimating and when the quantity of twists on the twist shaft is moderately little. This is likewise called direct radiating. It can likewise be utilized to make littler, transitional bars called warper’s pillars. These littler shafts are consolidated later at the slicing stage to create the weaver’s bar. This procedure is called radiating.
2.2.2 Ball Warping:
Ball warping is mainly used in manufacturing of denim fabrics. The warp yarns are wound on a ball beam in the form of a tow for indigo dyeing. After the dyeing process, the tow is separated and wound on a beam. This stage is also called long chain beaming or re-beaming.

2.3 Denim Dyeing:
The established pants were delivered out of indigo-colored Denim texture. The extraordinary character of this texture – just the twist string is colored makes it important to complete coloring in yarn structure. The yarns connected for Denim were solely created on ring turning machines in previous occasions. The advancement of OE yarns by applying littler rotors with a turning pace of up to 200 m/min has prompted the utilization of OE rotor yarns both for twist and weft. The yarns connected for weaving must be of high caliber, a high fiber for quality, consistency just as a little piece of short-stapled cotton filaments has a place with the fundamental highlights of the denim yarn. For normal pants characteristics the twist yarns are spun in a fineness of 50 to 90 Tex, for the weft yarn the fineness ranges are for the most part 75 to 120 Tex. On the off chance that Denim is made out of Tencel or Modal particularly for pants shirts the fineness’ are up to 25 Tex.
- Slasher Dyeing is used for Sheet Denim production.
- Rope Dyeing is used for Rope Denim production.
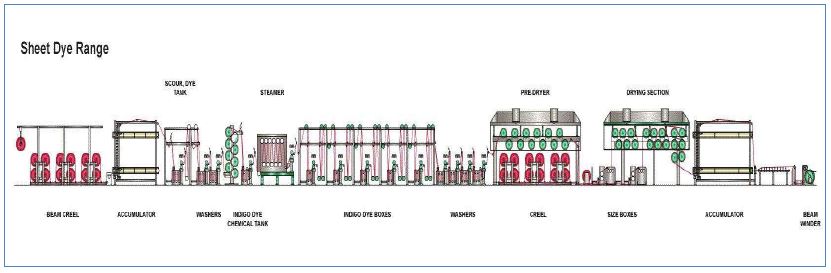
2.3.1 Slasher Dyeing:
In persistent slasher/sheet coloring and estimating machine, direct twisting shafts are utilized, rather than ball distorting signs if there should be an occurrence of Indigo rope coloring framework. The Slasher Dyeing machine is fit for dealing with Ne check structure 9/s to 30/s (OE and Slub both). Common schematic sheet coloring range is appeared in Figure. At the back end of the slasher/sheet coloring range, the immediate twisting bars are creeled. The yarns sheet from each pillar is pulled over and joined with the yarns from different shafts so numerous sheets of yarns can be made. When coloring as per the sheet coloring technique, rather than links the twist strings are nourished to the machine parallel by one another. These are a lot littler contrasted with the rope coloring machines. Another preferred standpoint is that the links don’t should be open subsequent to coloring.
Additionally, each yarn wets a lot quicker and along these lines diminishes the plunging and wetting times amid coloring. With everything taken into account, each string has a bigger surface contrasted with a coloring link and this requires fairly more hydro-sulphite to counteract an untimely oxidation of the indigo.
2.3.2 Rope Denim:
The indigo Rope coloring innovation for denim generation is viewed as an unrivaled coloring innovation, where better consistency of coloring is accomplished than other Indigo coloring advancements like slasher coloring. Indigo rope coloring was begun in USA. Today rope coloring represents a huge level of twist yarn colored for denim creation. The framework offers most elevated creation, because of nonstop procedure, as there is no stoppage for set changes. In this coloring strategy, greatest progression of shades and least peril of focus to selvedge shade variety can be accomplished. Stream outline of rope coloring is appeared in figure. Amid coloring process, it shapes a covering in the external layers of the cotton yarn and fiber. This creates a ring of shading around the cotton yarn, with the center stays white center. This coloring impact is known as ring coloring.

Indigo Rope Dyeing when dyeing according to the rope dyeing or cable dyeing method. 350 – 500 warp threads are bound on the ball warper to very thick cables of 10000 – 15000 m length. On the continuous dyeing installation, 12 to 36 cables are led side by side, wetted, dyed and dried after the dyeing process on cylinders and put into cans. Then the cables are dissolved to warps on the long chain beamer. The warps are added to the sizing machine, sized and then led together to warp depending on the total numbers of threads. In practice, this method has proven to be very good through obtaining an optimum indigo dyeing. However it is important that the cables have a constant tension in order to avoid warp stripes. The disadvantage compared to other methods is that yarn breakages do occur more often.
2.4 Long Chain Beamer:
After the rope coloring of twist yarn in denim generation, the following task is the Long Chain Beamer (LCB). At the point when the rope has been colored and dried in the rope coloring range, it is taken in expansive jars in coiler segment. In rope coloring range, in the event that the machine has a limit 24 ropes, at that point there will be 24 separate coilers which convey 24 ropes in discrete jars. These jars are exchanged to the Long Chain Beaming territory. The fundamental motivation behind long chain beamer is to open the rope into a sheet type of yarn and wind onto a warper shaft which thusly exchanged to the measuring machine.
In Long Chain Beamer, the yarn arrangement in the colored rope is change from a rope structure to a sheet structure. In the Long Chain Beamer the rope pull from the can by moving them upward to a managing gadget. The directing gadget is mounted over the can, most likely in the roof. The upward development of the rope enables the ropes to unravel before nearing the beamer head and enable the rope to shake free frame from the remainder of the rope in the can.
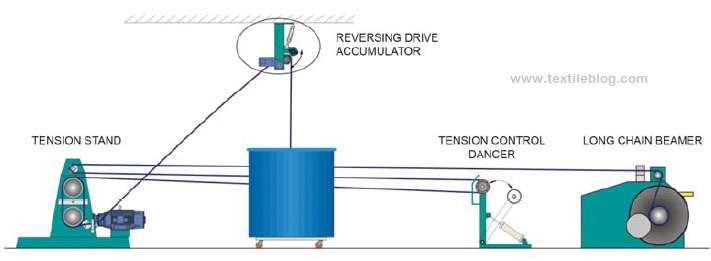
Process Flowchart for Long Chain Beamer:
Can
↓
Accumulator
↓
Tension Stand
↓
Tension Control Dancer
↓
Reed
↓
Counting Roller
2.5 Sizing
The process of applying a protective adhesive coating upon the yarn surface is called sizing. This is the most important operation to attain maximum weaving efficiency specially for blended and filament yarns.
2.5.1 Objects of Sizing:
- To improve the weave ability of warp yarn.
- To increase the tensile or breaking strength for cellulose yarn.
- To maintain good quality fabric.
- To reduce hairiness, weakness of textile materials.
- To remove electrolytic formation for synthetic or blended yarn.
- To increase elasticity.
2.5.2 Techniques of Sizing:
There are several techniques to impart size materials into the yarn. These are:
- Hot melt sizing
- Foam sizing
- High pressure sizing
- Electrostatic sizing
- Emulsion sizing
- Combined sizing
- Slasher sizing
2.5.3 Types of sizing according to application:
- Pure sizing: When sizing is done in yarn which produces unbleached fabric is called pure sizing. So, ingredients are on the weight of yarn 7 to 10%.
- Light sizing: This is used for dyeing and printing. 11 to 15% sizing ingredients are used on the weight of yarn.
- Medium sizing: For increase of strength and weight of the yarn 16 to 40% sizing ingredients are used on the weight of yarn.
- Heavy sizing: It is used to increase the weight of yarn. Above 40% sizing ingredients are used on the weight of yarn.
2.6 Weaving:
The way toward delivering a texture by intertwining twist and weft strings is known as weaving. The machine utilized for weaving is known as weaving machine or loom. Weaving is a craftsmanship that has been for a huge number of years. The soonest utilization of weaving goes back to the Egyptian human advancement. Throughout the years, both the procedure just as the machine has experienced exceptional changes. Starting today, there is a wide scope of weavers utilized, directly from the easiest handloom to the most complex loom.
2.6.1 Basic Weave Designs:
- Plain weave
- Twill weave
- Zig zag twill
- Herringbone twill
- Broken twill
2.6.2 Classification of Modern Weaving Machines:
Modern Weaving machines are classified according to their filling insertion mechanism. The classification is as follows:
- Rapier
- Projectile
- Air-Jet
- Water-Jet
2.7 Finishing Process:
In essential denim completing, texture touches base from weaving straightforwardly, without de-estimating, and is brushed to expel tainting, seared with fire to make the texture smoother by lessening shagginess, cushioned with a basic formula, disregarded a couple of skew moves to diminish texture torque which causes skew development and after that dried.
2.7.1. Objects of Finishing:
- To increase the attractiveness of fabric.
- To increase the service ability.
- To increase the beauty and brightness of fabric.
- To increase the fineness and to ensure smoothness.
- To ensure the softness of the fabric.
In Sinha denim ltd. there are two type of finishing process are used.
- Mechanical finishing
- Chemical finishing
Mainly two type of mechanical finishing are done in Sinha denim and rope denim ltd.
- Flat finishing
- Regular finishing
Difference between Flat finishing and Regular finishing is 4 wash box are used in flat finishing but no wash box in regular finishing process.
METHODOLOGY
3.1 Methodology:
Methodology is the systematic, theoretical analysis of the methods applied to a field of study. It also related to thesis topic that’s means research area and can be came with relative output theoretical analysis of the body of methods and principles associated with a branch of knowledge. Generally it related with new concept such as theoretical, practical and also qualitative techniques.
A methodology does now not set out to grant solutions – it is, therefore, now not the identical method. Instead, a methodology offers the theoretical more about for understanding a system procedure or set of methods, or best practices can be applied to specific case, for example, to carried output.
It has been defined also as follows:
- The analysis of the principles of methods, rules, and condition that employed by a discipline.
- Methodology also defined by systematic study that can be applied within a rules.
3.2 Productivity of Slasher Dyeing Denim:
In sheet or slasher denim production yarns come from warping section individually from the various sets of creel which make with various beam according to requirement . after that beam are set into creel zone of slasher denim machine and this beam came out with new beam which complete with dyeing and sizing simultaneously and after that it send to weaving zone to weave. For slasher denim process use direct warping system. During this process all yarn are carried out at a specific tension and stress.
Direct Warping
↓
Slasher Dyeing & Sizing
↓
Weaving
↓
Finishing
↓
Inspection
↓
Delivery
3.2.1 Productivity in Direct Warping:
Warping means to wind the yarn in a particular beam at a uniform tension and yarn are stay parallel. The productivity of warping depends on various parameter such as how many number of creel how many number of actual creel used and also depends on the running time of warping machine. If the machine are run with greater efficiency then it possible to make as requirement number of beam as set wise and usually use as much as 320 or 346 to make a beam of 22000 m or 11000m length and also requirement wise beam.

In direct warping machine we observed how much time to make a beam of required length to collect data.
Table: 01: Details Information about direct warping
| Sl. No | Cone Length (m) | Count | Total Warp Length (m) |
| D1 | 22000 | 7.2 RSL | 11000 |
| D2 | 11000 | 7RsL | 9250 |
| D3 | 23200 | 7.2RsL | 22000 |
| D4 | 21000 | 12 RSL+12R | 17500 |
| D5 | 18000 | 12 OE + 9 OES | 16250 |
3.2.2 Machine Specification of Direct Warping:
Different types of Machine shows different efficiency or productivity. In direct warping section we saw sucker muller machine which specification and we take data which giving below.
Table: 02: Machine Specification of Direct Warping
| Brand Name | Sucker Muller |
| Model | 2005 |
| Machine Serial No. | 100040161 |
| Origin | Germany |
| Working Width | 71″ |
| Manufacturing Year | 2005 |
| Max Beam Diameter | 140.9cm |
| Max Warping Speed | 850Mtr/min |
| Creel Type | H |
| Creel Capacity | 432 |
| Reed to Reed Distance | 0.8cm |
| Manpower | Six |
| Max Warping Capacity | 20000Mtr |
| Stop Motion | Auto |
3.2.3 Productivity in Slasher Denim Dyeing & Sizing:
In slasher denim dyeing &sizing process firstly start from creel. Creel content with set of beam, number of beam up to 16 or depends on requirement. When machine start unwinding of yarns start and passes through various couple of pressure roller or pad roller and different dye bath and also wash bath. Dyeing zone start from scouring bath. Slasher dyeing is continuous process. As a result yarn gets lots of stress from different roller and hit from heat and dyeing chemicals.
In slasher dyeing we observed how much time to make a beam of required length to collect data. We also talked with the machine operator, supervisor, production officers, Manager to find the wastage and to get the high efficiency. During observation we observed the information which is maintained by machine operator in register book of every shift.
Table: 03: Details Information about Slasher Dyeing & Sizing
| Sl. No | Warping Length (m) | Slasher Dyeing & Sizing Beam length (m) |
| D1 | 11000 | 11050 |
| D2 | 9250 | 9030 |
| D3 | 22000 | 21920 |
| D4 | 17500 | 17500 |
| D5 | 16250 | 15510 |
3.2.4 Machine Specification of Slasher Dyeing & Sizing
Production and product quality may vary on the basis of different brand’s machine action. Machine specification from which machine we took experimental data is given below-
Table: 04: Machine Specification of Slasher Dyeing & Sizing Machine.
| Brand Name | Sucker Muller |
| Origin | Germany |
| Creel Capacity | 16 |
| No. of color Dye Bath | 8 |
| No. of Size Bath | 1 |
| Total No. Of Box | 16 |
| Production Capacity | Continuous Dyeing Method |
| Storage Capacity | 1400Ltr |
| Stop Motion | Auto |
| Dye bath volume | 750 Ltr |
3.3 Rope Dyeing Denim:
Rope Dyeing is a denim dyeing process where the productivity of dyeing is higher than slasher dyeing process. In rope denim the quality of yarn dyeing is better and the production is high. 12 or 24 or 36 number of ball can be run at a time. The main benefit of rope dyeing process is here the variations of shade is less and quality of yarn is better because of better oxidation process system. In rope dyeing process use color is black, pure indigo, brown, sometimes use mixture of black-brown.
Ball Warping
↓
Rope Dyeing
↓
Long Chain
↓
Beam Sizing
↓
Weaving
↓
Finishing
↓
Inspection
↓
Delivery
3.3.1 Productivity in Ball Warping:
Ball Warping means to wind the yarn in a particular ball at a uniform tension and yarn are stay as a ball. The productivity of ball warping depends on various parameter such as how many number of creel how many number of actual creel used and also depends on the running time of ball warping machine. If the machine are run with greater efficiency then it possible to make as requirement number of beam as set wise and usually use as much as 420 to make a beam of 11000 m or 5500m length and also requirement wise beam. And the ends are 320 or more or less and the set is 2 or 3 three run at a time.
We are worked different shift to collect data. During our observation the machine speed is 450- 500 m/min. Experimental data are given bellow-
Table: 05: Details Information about Ball warping
| Sl. No | Cone Length (m) | Count | Total Ball Length (m) |
| B1 | 20000 | 7RsL | 11000 |
| B2 | 20000 | 9RsL | 11000 |
| B3 | 22000 | 7RsL | 5800 |
| B4 | 21000 | 7.2Rs +9 OE | 11000 |
| B5 | 18500 | 9Rs + 9OE | 8800 |
Table: 06: Machine Specification in Ball Warping
| Brand Name | West Point |
| Machine Serial No | WO#173725 |
| Origin | America |
| Working Width | 46″ |
| Manufacturing Year | 2005 |
| Max Beam Disc Diameter | 15″ |
| Max Warping Speed | 500Mtr/min |
| Creel Type | H |
| Creel Capacity | 448 |
| Stop Motion | Auto |
| Manpower | Six |
| Max Warping Length | 18500Mtr |
| Ball Width | 53″ |
3.3.2 Productivity in Rope Dyeing Machine:
In Rope dyeing process firstly start from ball stand or creel. Creel content with set of ball, number of ball is 12 or 24 or 36 or depends on requirement. When machine start unwinding of yarns start and passes through various couple of pressure roller or pad roller and different dye bath and also wash bath. Dyeing zone start from scouring bath. Slasher dyeing is a discontinuous process. As a result yarn gets lots of stress from different roller and hit from heat and dyeing chemicals. The dye bath capacity is 3000 liter. Here use mostly use Indigo or Vat dyeing sometimes use black or brown.
In Rope dyeing we observed how much time to complete a set of ball of required length to collect data. We also talked with the machine operator, supervisor manager to find the wastage and to get the high efficiency. During observation we observed the information which is maintained by machine operator in register book of every shift

Table: 07: Details Information about Rope Dyeing
| Sl. No | Total Ball Length (m) | Rope Dyeing Length (m) |
| B1 | 11000 | 11226 |
| B2 | 11000 | 11160 |
| B3 | 5800 | 5887 |
| B4 | 11000 | 11150 |
| B5 | 8800 | 8865 |
Table: 08: Machine Specification of Rope Dyeing
| M/C Name | Rope Dyeing M/C |
| Brand Name | Morrison |
| Origin | America |
| Dryer | 36 |
| Air Consumption | 60-70Kn |
| Model | 2007 |
| Manufacturing Year | 2007 |
| Creel Capacity | 24 |
| No. of Dye Bath | 10 |
| Total No of Box | 18 |
| Steam Supply | 5000-6000lb/hr. |
| Water Supply | 500-600lb/h |
| M/C Speed | 35Mtr/min |
| Production Capacity | Continuous Dyeing Method |
| Storage Capacity | 3000ltr |
| Stop Motion | Auto |
3.3.3 Productivity in Long Chain Beam:
The warp yarns are rope dyed, it is then necessary to change the yarn alignment from a rope form to a sheet form before entering the next process, which is slashing or sizing. Beaming or re- beaming involves pulling the ropes of yarn out of storage tubs and moving them upward to a guiding device. After the rope dyeing of warp yarn in denim production, the next operation is the Long Chain Beamer (LCB). The amount of wastage in long chain beam is near about 10-15 meter sometimes no wastage occurred.

Table: 09: Machine Specification of LCB
| Brand Name | West Point |
| Serial No. | WO#173733 |
| Origin | America |
| Max. Speed | 500 m/min |
| Max. Yarn Tension | 450 N |
| Working Width | 1,800 mm |
| Max. Beam Flange Diameter | 1000 mm |
| Stop Motion | Auto/Manual |
Table: 10: Details Information about LCB
| Sl. No | Rope Dyeing Length (m) | LCB Length (m) |
| B1 | 11226 | 11213 |
| B2 | 11160 | 11160 |
| B3 | 5887 | 58887 |
| B4 | 11150 | 11150 |
| B5 | 8865 | 8855 |
3.3.4 Productivity of Sizing:
After long chain beam process sizing process start and here creel system also. Rope dyeing yarn are passes through sizing chemical to give the strength. Here the amount of wastage is less or near about 15-20 meter. Sometimes the wastage is not occurred.
During experiment which machine we observed, that machine specification is given bellow-
Table: 11: Machine Specification Sizing
| Brand Name | Jupiter |
| Serial No. | 17480/7/2007 |
| Origin | India |
| Machine Speed | 40-80Mtr/min |
| No. of Squeeze Roller | 2 Pairs |
| No. of Size Dryer | 14 |
| Creel Capacity | 12 |
| Preparation Tank Temperature | 90°C |
| Cooking Time | 25-40 Minute |
| Manpower | Six |
Table: 12: Details Information about sizing:
| Sl. No | LCB Length (m) | Sizing Length (m) |
| B1 | 11213 | 11300 |
| B2 | 11160 | 11200 |
| B3 | 58887 | 5920 |
| B4 | 11150 | 11200 |
| B5 | 8855 | 8905 |
3.4 Productivity in Weaving:
Weaving section of Sinha denim and rope denim limited are dived into two floor but two floor work with same reference and style number at a time that’s means rope dyeing yarn and slasher dyeing yarn are weaving process are same not different way. The weaving process are start from unwinding of sizing yarn then shedding picking beat up process and finally rolling the fabric into cloth roller. The wastage amount in weaving process is near about 8-10 meter or sometimes none when staring or stop. The machine are run 600-700 RPM and the efficiency of machine is high because of low wastage and breakage and the use machine is Air-jet. Crimp% is stay between 12-14%. Sometime causes of improper sizing breakage increase during weaving and the quality of fabric decrease.
Table: 13: Machine Specification of Weaving
| Brand Name | Picanol |
| Model | PICANOL OMNI Plus 800 |
| Origin | Belgium |
| Machine Speed | 850 rpm |
| Reed | Profile Reed |
| Shedding | Tappet Shedding Mechanism |
| Air Pressure | 9.5bar |
| Total Relay Valve | 14 |
| Number of Heald Shaft | 4 |
| Number of cutter | 2 |
| Let Off Motion | Electrical |
| Take Up Motion | Electrical |
3.4.1 Details Information From in Weaving Section:
We are two member of our group worked at the Weaving floor in the industry to collect data of production.
Table:14 Details Information about Weaving Section (Slasher Dyeing)
| SL. No | Fabric Construction | Warping | Dyeing & Sizing Warp | Weaving, Fabric | ||||
| EPI | PPI | Warp Count | Weft Count | Length (M) | Length (M) | Length (yds) | Crimp% | |
| D1 | 60 | 45 | 7.2 RSL | 10L-40DSL+ 300L-40D | 11000 | Beam No-1 = 1000 Beam No-2 = 2000 Beam No-3 = 2000 Beam No-4 = 2000 Beam No-5 = 2000 Beam No-6 = 2050
Total length = 11050 | Beam No-1 = 925 Beam No-2 = 1933 Beam No-3 = 1948 Beam No-4 = 1951 Beam No-5 = 1949 Beam No-6 = 1979 Total length = 10685 | 12% |
| (Total length = 9803 Meter) | ||||||||
| D2 | 62 | 40 | 7 RSL | 8L-40D | 9250 | Beam No-1 = 1850 Beam No-2 = 1850 Beam No-3 = 1850 Beam No-4 = 1850 Beam No-5 = 1630 Total length = 9030 | Beam No-1 = 1751 Beam No-2 = 1765 Beam No-3 = 1739 Beam No-4 = 1743 Beam No-5 = 1527 Total length = 8525 | 15.5% |
| (Total length = 7821 Meter) | ||||||||
| D3 | 60 | 45 | 7.2 RSL | 10L-40DSL+ 300L-40D | 22000 | Beam No-1 = 2000 Beam No-2 = 2200 Beam No-3 = 2200 Beam No-4 = 2200 Beam No-5 = 2120 Beam No-6 = 2000 Beam No-7 = 2200 Beam No-8 = 2200 Beam No-9 = 2200 Beam No-10 = 2600 Total length = 21920 | Beam No-1 = 1950 Beam No-2 = 2164 Beam No-3 = 2153 Beam No-4 = 2132 Beam No-5 = 2028 Beam No-6 = 1922 Beam No-7 = 2141 Beam No-8 = 2131 Beam No-9 = 2147 Beam No-10 = 2574 Total length = 21342 | 12% |
| (Total length = 19580 Meter) | ||||||||
| D4 | 72 | 53 | 12RSL+12 R | 16L-40D | 17500 | Beam No-1 = 2200 Beam No-2 = 2200 Beam No-3 = 2200 Beam No-4 = 2200 Beam No-5 = 2200 Beam No-6 = 2200 Beam No-7 = 2200 Beam No-8 = 2100 Total length = 17500 | Beam No-1 = 2131 Beam No-2 = 2141 Beam No-3 = 2158 Beam No-4 = 2180 Beam No-5 = 2150 Beam No-6 = 2130 Beam No-7 = 2059 Beam No-8 = 2020 Total length = 16970 |
12.41% |
| (Total length = 15569 Meter) | ||||||||
| D5 | 72 | 48 | 12 OE +9 OES | 10Rsl+300L40D | 16250 | Beam No-1 = 2800 Beam No-2 = 2600 Beam No-3 = 2700 Beam No-4 = 2700 Beam No-5 = 2700 Beam No-6 = 2010 Total length = 15510 | Beam No-1 = 2675 Beam No-2 = 2370 Beam No-3 = 2457 Beam No-4 = 2472 Beam No-5 = 2540 Beam No-6 = 1819 Total length = 14333 | 18.3% |
| (Total length = 13106.2 Meter) |
Table:15 Details Information about Weaving Section (Rope Dyeing)
| SL. No | Fabric Construction | Ball Warping | Dyeing | LCB | Sizing | Weaving, Fabric | ||||
| EPI | PPI | Warp Count | Weft Count | Length (M) | Length (M) | Length (M) | Length (M) | Length (yds) | Crimp % | |
| B1 | 66 | 44 | 7RsL | 10L 40D | 11000 | 11226 | 11213 | B/N 1 = 1500 B/N 2 = 1400 B/N 3 = 1400 B/N 4 = 1400 B/N 5 = 1400 B/N 6 = 1400 B/N 7 = 1400 B/N 8 = 1400 Total length =11300 | B/N 1 = 1391 B/N 2 = 1266 B/N 3 = 1290 B/N 4 = 1272 B/N 5 = 1290 B/N 6 = 1279 B/N 7 = 1305 B/N 8 = 1296
Total length = 10389 | 18.6 % |
| Total length = 9500 (meter) | ||||||||||
| B2 | 54 | 44 | 9RsL | 6 OE | 11000 | 11160 | 11160 | B/N 1 = 1850 B/N 2 = 1850 B/N 3 = 1850 B/N 4 = 1850 B/N 5 = 1850 B/N 6 = 1950 Total length =11200 | B/N 1 = 1785 B/N 2 = 1809 B/N 3 = 1804 B/N 4 = 1787 B/N 5 = 1820 B/N 6 = 1914
Total length =10919 | 12.2% |
| Total length = 9985 (Meter) | ||||||||||
| B3 | 54 | 44 | 7 RsL | 6 OE | 5800 | 5887 | 5887 | B/N 1 = 1500 B/N 2 = 1500 B/N 3 = 1450 B/N 4 = 1470 Total length =5920 | B/N 1 = 1440 B/N 2 = 1452 B/N 3 = 1409 B/N 4 = 1447 Total length =5748 | 12.6% |
| Total length = 5256 (Meter) | ||||||||||
| B4 | 60 | 48 | 7.2Rs +9 OE | 10L 40D | 11000 | 11150 | 11150 | B/N 1 = 1900 B/N 2 = 1900 B/N 3 = 1900 B/N 4 = 1900 B/N 5 = 1900 B/N 6 = 1700 Total length | B/N 1 = 1756 B/N 2 = 1859 B/N 3 = 1851 B/N 4 = 1855 B/N 5 = 1860 B/N 6 = 1654
Total length = | 13% |
| =11200 | 10835 | |||||||||
| Total length = 9908 (Meter) | ||||||||||
| B5 | 60 | 52 | 9 Rs +9 OE | 14L+40DSlub | 8800 | 8865 | 8855 | B/N 1 = 1500 B/N 2 = 1500 B/N 3 = 1465 B/N 4 = 1500 B/N 5 = 1500 B/N 6 = 1440 Total length =8905 | B/N 1 = 1448 B/N 2 = 1450 B/N 3 = 1432 B/N 4 = 1462 B/N 5 = 1468 B/N 6 = 1410 Total length = 8670 | 12.2% |
| Total length = 7928 (Meter) |
3.5 Productivity in Finishing:
Finishing is a process which is one of the most important and essential process for fabric production. The main objective of finishing is to make the surface of fabric More Smooth.
Our internship period we saw Morrison machine is use for finishing.in this machine for finishing purpose use Proper finishing method is crucial in any other case the material will be rejected with the aid of the buyer for this reason use mercerization, skewing, brushing, singeing, and also use calendaring process. In case of denim generally controlling of the shrinkage and the skew of the fabric is done. Besides, finishing technique ending area have to do a lot of others process like fabric storing, inspection etc. So a finishing area in a denim industry performs important role. In slasher and rope denim finishing process, same ending computing device is used and equal manner also. Sometimes use stenter machine According to buyer require requirements cloth (finished) characteristics parameters i.e. Shrinkage percentages, heat placing, increase the width of the fabric etc. are set up in the machine.
Table:16 Machine Specification Of Finishing
| Brand Name | Morrison |
| Serial No. | T98 |
| Origin | America |
| Model | M80SF |
| Manufacturing Year | 2006 |
| Power | 65.5KW |
| Machine Length × Width | 105m × 1.83m |
| Shrinkage Control Warp/Weft/ Lycra | 10-15/5-7/20-25% |
| Machine Capacity | 80Mtr/min |
Table:17 Details Information About Finishing Section
| SL. No | Weaving Length (m) | Finish Length (m) | Shrinkage % | Skewing |
| D1 | 9803 | 8623 | 12 | 10 cm |
| D2 | 7821 | 6805 | 13 | 10 cm |
| D3 | 19580 | 17035 | 13 | 10 cm |
| D4 | 15569 | 13700 | 12 | 10 cm |
| D5 | 13106.2 | 11402 | 13 | 12 cm |
| R1 | 9500 | 8360 | 12 | 12 cm |
| R2 | 9985 | 8687 | 13 | 10 cm |
| R3 | 5256 | 4625 | 12 | 11 cm |
| R4 | 9908 | 8626 | 13 | 10 cm |
| R5 | 7928 | 6898 | 13 | 10 cm |
3.6 Inspection:
Fabric inspection is a process in where inspect the fabric to find out the fabric faults and grade the fabric A, B, A grade means higher quality of fabric, B grade means less better quality. And here using method is 4 point system. By using the method anyone can find out the faults of fabric such as starting mark, miss ends, double picks, knots and also various kinds of faults which came from dyeing or other process. During our internship process we saw STT machinery and lighting system. Four tube lights are provided to optimize the lighting. Measuring counter is provided in front of the inspection table for controlling length. It has forward, reverse, start and stop button controls. The cloth is pulled over the white board table by a variable speed motor and different cloth defects are recorded for quality control purpose. After inspection fabric is wound on roller.
Table:18 Machine Specification of Inspection
| Name | Inspection Machine |
| Brand | STT Machinery |
| Model | Amoeba |
| M/C Dimension | 2580mm x 2920mm x 2310mm (L×W×H) |
| Speed | 0 – 80yds/min |
| Size of Inspection Board | 860mm (height |
| Motor Power | 3 HP |
| Roller Width | 72″ |
| Fabric Roll Diameter | 450m |
| Fabric Roll Length | 90-102 M |
Table:19 Details Information About in Inspection Section
| SL. No | Finish Length (m) | Inspection Length (m) | Percentage (%) |
| D1 | 8623 | A-Grade =5343 B-Grade = 3274.5 Total length = 8617.5 | A=62 % B=38 % |
| D2 | 6805 | A-Grade = 3740 B-Grade = 3060 Total length = 6800 | A=55 % B=45 % |
| D3 | 17035 | A-Grade = 10728 B-Grade = 6300 Total length = 17028 | A=63 % B-=37 % |
| D4 | 13700 | A-Grade = 7943 B-Grade = 5751 Total length = 13694 | A=58 % B=42 % |
| D5 | 11402 | A-Grade = 5926 B-Grade =5460 Total length = 11386 | A=52 % B=48 % |
| R1 | 8360 | A-Grade = 4347 B-Grade = 3900 Total length = 8247 | A= 53 % B= 47 % |
| R2 | 8687 | A-Grade = 4862 B-Grade = 3800 Total length = 8662 | A= 56 % B= 44 % |
| R3 | 4625 | A-Grade = 2402 B-Grade = 2218 Total length =4620 | A= 52 % B= 48 % |
| R4 | 8626 | A-Grade = 4479 B-Grade = 4130 Total length = 8609 | A= 52 % B =48 % |
| R5 | 6898 | A-Grade = 4138 B-Grade = 2758 Total length = 8696 | A=48 % B= 52 % |
DISCUSSION
4.1 Productivity Analysis of Slasher Dyeing Denim
4.1.1 Productivity Direct Warping Section:
In direct warping section, needs 60-85 minutes time for winding 22000 meter length of yarn whereas machine speed is 500-550 m/min. And the average machine stoppage is 6-8 times. By means of machine speed, it seems to be knotting time is 20-22 minutes. But initial stage of production running machine speed is lower as well as each breakage take 3+ minutes time, when machine is stopped. As a result actual time is more than calculating time.
From the observed data, it is seen that breakage is occurred due to spinning fault of yarn and warping. Between these two reasons 55% stoppage is responsible for spinning faults whereas 45% is warping fault. In direct warping section the majority of machine stoppage occur due to loose yarn, bad knotting, bad slub, pig tail, entanglement, cut cone, thin place, tension variation, dust, weak yarn etc.
From the observation data of direct warping section, we have discussed about it. We can say the following comments-
- Average machine stoppage Rate: Average machine stoppage rate in direct warping for denim production is 4-6 times respect to regular length, number of ends and yarn count.
- Machine Speed Variation: Speed variation of machine is largely effect on yarn breakage in direct warping for denim production. For high speed of machine, machine stoppage is more. In direct warping machine, the average machine speed is 500-550 m/min to maintain the better production.
- Design of the Creel: H creel is used in the direct warping normally. By means of H-creel yarn path angle is dispatched from 180 degree which causes yarn separation by dint of tension variation. So, to reduce tension variation and increasing the production V-creel should be used.
- Tension Variation: Tension control is very important matter in warping. If the tension variation is increase from each other, the possibility of yarn separation will increase.
*During our Data collection in direct warping section about productivity we saw that wastage of yarn from cone to beam is near about 120-180 meter.
Moreover after discussion with factory floor personnel e.g. machine operator, supervisor, production officer and manager that the following wastage are frequently occurred.
Productivity loss due to Mechanical Reasons:
- Uneven warp beam
- Unequal length
- Piecing.
- Soft end on the warping beam.
- Faulty Yarn guide
- Reed fault
- Faulty drums
- Faulty beam flange
Operational Reasons:
- Speed variation
- High Speed
- Winding angle
- Yarn path angle
- Snarl formation in the warp
- Broken ends
- Unequal length of warp
- Unequal size or weight of cone or cheese in the creel.
4.1.2 Productivity in Slasher Dyeing & Sizing Section:
Slasher dyeing & Sizing is a continuous process whereas machine speed is 20-25 m/min.
From the observation data, we have known that machine productivity rate is loss due to machine speed, abrasion, loose yarn, faulty yarn, weak yarn, tight package of beam, tension variation, improper roller pressure etc.
From the observation data of slasher dyeing section, we have discussed about it. We can say the following comments-
- Reasons of Majority production loss: In slasher dyeing section the majority production loss occur due to excessive machine speed, abrasion, loose yarn, faulty yarn, weak yarn, tight package of beam, tension variation, improper roller pressure etc. Moreover some other problem of process and mechanical faults also responsible for yarn breakage.
- Tension Variation: Tension control is very important matter. If the tension variation is increase from each other, the possibility of yarn breakage will increase. To reduce yarn breakage, tension variation should be reduced.
- Chemical concentration: Most of the time chemical concentration largely effect on production loss.
- Temperature of Dryer: Up to a limited temperature fiber/yarn can bare. When temperature is high fiber will be damaged and shade variation occurred.
Moreover after discussion with factory floor personnel e.g. machine operator, supervisor, production officer and manager that the following faults are frequently occurred in slasher dyeing section but we did not find during our study.
Mechanical Reasons:
- Defective machine parts
- Faulty cylinder surface
- Faulty roller surface
Operational Reasons:
- Excessive machine speed
- Improper and uneven tension
- Due to chemical concentration
- Excessive drying
- Stoppage of the machine
- Hard sizing or excessive concentration of sizing
- Miss calculation during making recipe
- Improper viscosity
*Slasher dyeing & Sizing process productivity loss rate is near about 380-400 meter for the reason of machine stoppage, shade variations and also set change.
4.2 Productivity Analysis in Rope Denim
4.2.1 Productivity in Ball Warping Section:
In ball warping section, needs 45-50 minutes time for winding 5500 meter length of yarn whereas machine speed is 300-350 m/min. And the average machine stoppage is 3-4 times. By means of machine speed, it seems to be that the actual time 20-25 minutes. But initial stage of production running machine speed is lower as well as each breakage take around 3 minutes time, when machine is stopped. As a result actual time is more than calculating time.
In ball warping section the majority of yarn break occur due to loose yarn, bad knotting, bad slub, pig tail, entanglement, cut cone, thin place, tension variation, dust, weak yarn etc.
From the observation data of ball warping, we have discussed about productivity. From where we can say the following comments-
- Machine Speed Variation: Speed variation of machine is largely effect on in ball warping for denim production. In ball warping machine, the average machine speed is 300-350 m/min to maintain the production simultaneously control of loss of production.
- Reasons of Majority Breakage: In ball warping section the majority yarn breakage occur due to cut cone, loose yarn, bad knotting, bad slub, pig tail, entanglement, thin place, tension variation, dust, weak yarn etc. Moreover some other problem of process and mechanical faults also responsible for yarn breakage.
- Tension Variation: Tension control is very important matter in warping. If the tension variation is increase from each other, the possibility of yarn breakage will increase. In ball warping use pressure is 50-70 KN.
After discussion with factory floor personnel e.g. machine operator, supervisor, production officer and manager that the following loss rate are frequently occurred in ball warping section.
Mechanical Reasons:
- Unequal length
- Piecing.
- Faulty Yarn guide
- Reed fault
- Faulty beam flange
- Faulty drum
Operational Reasons:
- High Speed
- Winding angle
- Yarn path angle
- Unequal size or weight of cone or cheese in the creel.
*During our Data collection in ball warping section about productivity we saw that wastage of yarn from cone to beam is near about 150-200 meter some time
4.2.2 Productivity in Rope Dyeing Section:
In rope dyeing process average machine stoppage is 2-3 times whereas machine speed is 25 m/min and 11000 meter length of yarn.
From the observation data, we have known that production loss due to machine speed, abrasion, loose yarn, faulty yarn, weak yarn, tight package of beam, tension variation, improper roller pressure etc.
From the observation data of rope dyeing section, we have discussed about it. We can say the following comments-
- Tension Variation: Tension control is very important matter. If the tension variation is increase from each other, the possibility of shade variations increase. To reduce this tension variation should be reduced.
- Chemical concentration: Most of the time chemical concentration largely effect on yarn production. If the concentration is high or less that time it effects on production loss.
- Temperature of Dryer: Up to a limited temperature rope can bare. When temperature is high, fiber will be damaged and yarn may break. This is why in rope dyeing section 36 dryer are divided into 3 groups. First group of dryers consist of 120-1300C, second group of dryers consist of 115-1200C and third group of dryers consist of 90-1000C.
Moreover after discussion with factory floor personnel e.g. machine operator, supervisor, production officer and manager that the following faults are frequently occurred in rope dyeing section but we did not find during our study.
Mechanical Reasons:
- Defective machine parts
- Insufficient care of machine
- Faulty cylinder surface
- Faulty adjustment
- Faulty roller surface
- Faulty padder surface
Operational Reasons:
- Weak warp yarn
- Due to chemical concentration
- Due to excess operational time
- Excessive drying
- Tight package of beam
*During our working session we are not find any wastage in rope dyeing process except mechanical problem but we saw elongation of yarn range is 1.5%-1.8%
4.2.3 Productivity in LCB Section:
In Long Chain Beamer, the yarn alignment in the dyed rope is change from a rope form to a sheet form. In this process yarn are separate from ball formation to sheet formation ends range from 320-380. In the Long Chain Beamer the rope pull from the can by moving them upward to a guiding device. As a result few amount of wastage is occurred
From the observation data, we have known that production loss occurred due to machine speed, abrasion, loose yarn, faulty yarn, weak yarn, tight package of beam, tension variation, improper roller pressure etc.
From the observation data of rope dyeing section, we have discussed about it. We can say the following comments-
- In rope dyeing there is a possibility to repair broken end in LCB (Long Chain Beamer).
- Before beaming in LCB, it removes/repairs broken yarns of pre-stages (Ball warping & rope dyeing).
- LCB action like as beam warping, most of the yarn breakage reasons is similar as beam warping.
Moreover after discussion with factory floor personnel e.g. machine operator, supervisor, production officer and manager that the following faults are frequently occurred in LCB section.
Mechanical Reasons:
- Defective machine parts
- Insufficient care of machine
- Faulty adjustment
- Unwanted machine stoppage
Operational Reasons:
- Faulty preparation of warp
- Excessive or insufficient drying
- Wrong threading arrangement
*In the Long Chain Beamer the rope pull from the can by moving them upward to a guiding device. As a result few amount of wastage is occurred sometime.
4.2.4 Productivity in Sizing Section:
In sizing average machine speed is 20-25 m/min. From the observation data, we have known that majority production loss occurred due to machine speed, hard sizing, high temperature and high squeeze roller pressure and yarn fault.
From the observation data of sizing section, we have discussed about breaking fault. From where we can say the following comments-
- Machine Speed Variation: Speed variation of machine is largely effect on yarn that cause the production loss during sizing for denim production. For high speed of machine, yarn separation is more. In sizing machine, the average machine speed is 20-25 m/min to maintain the production.
- Chemical concentration: Most of the time chemical concentration largely effect on production.
- Temperature of Dryer: Up to a limited temperature fiber/yarn can bare. When temperature is high fiber will be damaged and yarn may break. Temperature range for sizing is about 90⁰C
Moreover after discussion with factory floor personnel e.g. machine operator, supervisor, production officer and manager that the following faults are frequently occurred in sizing section.
Mechanical Reasons:
- Defective machine parts
- Insufficient care of machine
- Faulty cylinder surface
- Faulty adjustment
- Unwanted machine stoppage
Operational Reasons:
- Excessive machine speed
- Improper and uneven tension
- Hard sizing or excessive concentration of sizing
- Excessive or insufficient drying
- Miss calculation during making recipe
- Improper viscosity
- Excessive squeeze roller pressure
- Hardness of squeeze roller
*In sizing process wastage is near about 15-20 meter and yarn are elongated this percentage is 0.5-0.8%
4.2.5 Productivity in Weaving Section:
Weaving is done after sizing & dyeing process. Sometimes yarn are came from Rope dyeing or sometimes are came from slasher dyeing process. In both process weaving are same and complete by picanol omniplus800. Average warp yarn break is 10-12 times and weft yarn breakage is 10-15 times for near about 2200 meter length of fabric whereas machine rpm is 750- 800.
From the observation data, we have known that majority production loss is occurred due to excessive machine speed, weak weft yarn, excessive air pressure, damaged yarn in the dyeing or sizing section, faults of worker, faulty preparation of warp, repeating warp streaks, thin place, hard sizing or excessive concentration of sizing, insufficient care of machine etc.
From the observation data of weaving section, we have discussed about production loss. From where we can say the following comments-
- Production loss rate: Production loss rate of direct dyeing is higher than the Rope dyeing. Because the individual yarn tension varies during direct dyeing. But the individual yarn tension of rope dyeing remains same. For this reason the yarn break during weaving is higher than the rope dyeing.
- Machine Speed Variation: Speed variation of machine is largely effect on breakage rate during weaving for denim production. The average machine speed is 700-750 rpm to maintain the production.
- Reasons of Majority production loss: During weaving the majority yarn breakage occur due to yarn fault and tension variation. Moreover some problem of process and mechanical faults also responsible for yarn breakage which the main causes of production loss.
- Backrest Roller Setting: Due to backrest roller setting the yarn breakage is also ups and down. For the higher count yarn the backrest keep parallel. But for the lower count backrest keep higher position for making higher tension.
- Air Pressure: Due to excessive air pressure the filling yarn may break down. If the pressure is so high, the will break. But if the pressure is low the filling yarn will not reach properly to the other end. Air pressure is 6 bar.
Moreover after discussion with factory floor personnel e.g. machine operator, supervisor, production officer and manager that the following faults are frequently occurred in weaving section.
Mechanical Reasons:
- Defective machine parts
- Insufficient care of machine
- Faulty adjustment
- Faulty setting of backrest according to yarn count
- Rough surface of drop wire
Operational Reasons:
- Excessive machine speed
- Improper and uneven tension upon the warp yarn
- Faulty preparation of warp
- Bad sizing
- Bad knotting
- Thick place & thin place
Others Reasons:
- Relative humidity
- Moisture content
- Due to unskilled worker
*In weaving section wastage rate is lower. It’s near about 8-10 meter when machine start (knotting time) another is when process finished time. It’s near about 5-10 meter.
4.2.6 Productivity in Finishing Section:
Finishing process is one of the most important and essential process for production of good end product. In general, before marketing the final product, all the process which is applied on the fabric after weaving is called finishing. Two types of finishing process are usually done. In our working session we saw that chemical finishing such as mercerization, softening, and different types of wash both cold and cold wash. In mechanical finishing brushing, singeing, calendaring process are done for make the surface more smooth.
Another finishing process is sanforizing. The sole objective of Sanforizing is to control the length wise shrinkage of fabric. The purpose of the process is to shrink fabrics in such a way that textiles made up of these fabrics do not shrink during washing. The amount of potential wash shrinkage must be determined prior to shrinking. So, there is nothing very variation in finishing section in both fabric rope and sheet. Slightly variation we found that, in rope fabric finishing. Actually finishing process are done according to buyer requirement.
*In finishing process shrinkage percentage vary from 10-12% for heat setting fabric another is 10-13% for regular fabric and the skewing is 10-12 cm
4.2.7 Productivity in Inspection:
In inspection section fabric quality are checked or faults measured by 4 points system method. This fabric are came from weaving after completing both rope dyeing and sheet dyeing process. Quality of rope dyeing fabric is better than sheet dyeing process. Because of here shade variation are less and machine stoppage rate are less that are free from various kinds of defects. In inspection section fabric inspect in three categories A, B, C. 52-68% are A categories fabric are found sometimes more or less and 20-40% are found B categories fabric and C categories fabric are not counted.. Every single yard of the denim goes through inspection department and rated by a point count system to ensure that quality is up to standard before packing. Defective fabric pieces are rejected and sold as seconds and relatively minor defective points are marked clearly using stickers. In inspection section Input is finished fabric & output is inspected fabric roll.
You may also like: Quality Issues in Denim Production
*In Inspection section the amount of wastage is a little bit when the new fabric joint are came that time wastage is 12-15 inch. The amount of wastage is near about 0.5-1 meter when rolling the fabric.
Conclusion:
Finally At the end of our thesis we came to know that productivity of Rope Denim is more than Sheet Denim. Production loss is more in direct warping compare to ball warping. Also in sheet dyeing production loss rate is more compare to rope dyeing, here wastage rate occurs due to roller pressure variation, excessive drying etc. In rope dyeing sizing production loss rate is less compare to sheet dyeing sizing. This loss rate due to size pickup percent is more, stoppage of machine, too much drying etc. Sheet dyeing yarn are when weave that time productivity is loss more compare to rope dyeing weaving. In weaving section loss rate increase because of excessive air pressure, weft breakage, weak yarn, sizing defects. we have come to find out that if some of rate of loss can be reduced by maintaining proper system in every section and also by reducing such as like as , less faulty yarns, reduce impurities, regular maintenance, worker awareness, on production quality check etc. If the rate of productivity increase that will be earn more profit for the company, time will be saved, and quality of the product will improve. Market value of the company will also improve. It is a great part a company should well maintain for their own benefit.
References:
- Clariant Denim Book
- https://nptel.ac.in/courses/116102005/
- https://www.scribd.com/doc/71096919/Project-Report-on-Fabric-Production-Arvin
- http://www.assignmentpoint.com/science/textile/industrial-training-in-opex-and- sinha-textilegroup.html
