What is Operation Breakdown?
The work in each style is broken down into operations. An operation is one of the processes that must be completed in converting materials into finished garments. An operation breakdown is a sequential list of all operations involved in assembling a garment, component or style. The sheet of listed operations of a style is also known as operation breakdown (OB). The operation breakdown is done to understand garment construction – like stitch class and seam types used in making the sample garment. Some times operation breakdown is also called garment operation bulletin. Though garment operation bulletin includes more information than the operation breakdown.
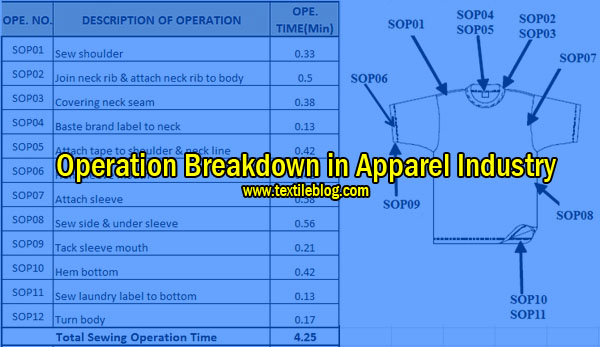
An operation breakdown in apparel industry contains following information:
- Name of the machines to use for doing the specific operations
- Sewing and non-sewing operations
- Estimated time to do each operation for one unit
Benefits of breakdown in apparel industry:
- Could notice all operations of the garment at a time.
- Could expect the difficulties of doing a crucial operation.
- Could make layout in an easy, simple and less time-consuming way.
- Could calculate the SMV for target setting and equal time distribution to the operator during layout.
- Easy to select appropriate operator for the specific process.
- Could know the quantity and kind of machine required to produce the required garment.
- Could achieve the production target within a very short period.
- Could be aware about quality to meet the buyers standard.
- Could know about additional guide, folder and attachment.
How to make operation breakdown for apparel industry?
Operation breakdown is a primary tool of industrial engineering. It helps to set a production line with correct number of machines and manpower. For making operation breakdown in apparel industry below steps have to follow:
- Step 1: Preparing an OB format.
- Step 2: Collection of correct Sample
- Step 3: Making operation breakdown for the sample
- Step 4: Define machine for each operation
- Step 5: Enter SMVs for each operation
- Step 6: Calculate production per hour
- Step 7: Calculate number of machines
- Step 8: Calculate estimated production per hour
- Step 9: Calculate machine summary
Sample operation breakdown of men’s shirt:
| SI. No. | Operations | SMV | Machine Type |
| Collar | |||
| 1 | Collar pieces pint 2 | 0.60 | SNIS |
| 2 | Collar run stitch | 0.42 | SNIS |
| 3 | Collar trim and turn | 0.25 | SNEC |
| 4 | Collar top stitch | 047 | SNIS |
| 5 | Band hem | 0.34 | SNIS |
| 6 | Band set | 0.65 | SNIS |
| 7 | Collar label attachment | 0.24 | SNIS |
| 8 | Band top | 0.45 | SNIS |
| 9 | Band and collar ready trim | 0.41 | SNEC |
| Cuff preparation | |||
| 10 | Cuff pieces joint 2 | 0.80 | SNIS |
| 11 | Cuff hem | 0.53 | SNIS |
| 12 | Cuff run stitch | 0.73 | SNIS |
| 13 | Cuff trim and turn | 0.57 | SNEC |
| 14 | Cuff top and sleeve pleat making | 0.66 | SNIS |
| Sleeve preparation | |||
| 15 | Sleeve panel attach | 0.70 | OLS |
| 16 | Sleeve panel top | 0.65 | SNIS |
| 17 | Under placket attach and tacking | 0.65 | SNIS |
| 18 | Big placket attachment | 1.18 | SNIS |
| Front | |||
| 19 | Button hole placket trim and attachment | 0.56 | KANSAI |
| 20 | Button placket sew and wash care label | 0.38 | SNIS |
| 21 | Button placket piping attach | 0.40 | SNIS |
| Back | |||
| 22 | Label attachment | 0.35 | SNIS |
| 23 | Yoke attach and top | 043 | SNIS |
| 24 | Dart mark and sew | 0.56 | SNIS |
| 25 | Front and back trim and pair | 0.70 | MANUAL |
| Assembly | |||
| 26 | Shoulder attachment and top | 046 | SNIS |
| 27 | Collar attach | 0.54 | SNIS |
| 28 | Collar finishing with content label | 0.85 | SNIS |
| 29 | Sleeve no set and attach | 0.85 | OIS |
| 30 | Top stitch at armhole | 0.71 | SNIS |
| 31 | Side seam attach and sleeve trim | 0.70 | OL5 |
| 32 | Cuff no set and attaching | 0.88 | SNIS |
| 33 | Bottom hem B\S and B\H | 0.67 | SNIS |
| 34 | Buttonhole front-7, cuff-2, sleeve placket 2 | 1.08 | BH |
| 35 | Button mark | 0.27 | MANUAL |
| 36 | Button front -7, spare-1, cuff 2, sleeve placket 2 | 1.17 | BTN |
| 37 | Button melting | 0.23 | IRON |
| TOTAL | 22.10 |
Calculation of operation breakdown:
……………………………..Worker x Working hour x 60
Target per hour = ——————————————– x Efficiency %
…………………………………………….SMV
…………………………………………………..SMV
Basic Pitch Time (BPT) = ——————————–
…………………………………………..Total Manpower
……………………………………………………………………….BPT
Upper Control Limit (UCL) = ————————————————————————–
………………………………………………….Wanted Organizational Efficiency (0.85)
Lower Control Limit (LCL) = BPT x 2 – UCL
References:
- Apparel Manufacturing Technology by T. Karthik, P. Ganesan, and D. Gopalakrishnan
- Practice of Garments Merchandising and Management by Engr. Md. Faruk Hosen
- https://textilelearner.net/operation-of-sewing-section-process-breakdown-of-basic-shirt/
- http://garmentsdiary.com
- http://textilestorage.blogspot.com
You may also like: Efficiency and Productivity of Sewing Line
