Combing Action:
Combing is a process which is introduced into the spinning of finer and high-quality yarns from cotton. It is carried out in order to improve the quality of the sliver. The carded materials (sliver) contain certain amount of short fibers, neps, fine kitty and leaf particles. Short fibers are a hindrance to spinning of finer counts where the number of fiber in the cross section of the yarn is less. The short fibers cause thick and uneven places in the yarn length and the yarn looks hairy. Apart from this, very short fibers do not contribute anything to yarn strength. Short fibers below a certain pre-determined length can be easily separated out by using comber machine.

Objects of Comber:
To remove the short fibers below a pre-selected length so that the spinner enable to produce finer or better quality of yarn that cannot be possible in carding state.
- Elimination of remaining impurities.
- Elimination of large proportion (not all) of the neps in the fiber.
- Formation of sliver having maximum possible evenness.
- To straighten the fibers.
Contribution of Comber to Yarn Quality:
- To improve the uniformity and strength
- Improve the spinning value of fiber.
- Reduce the neps in the yarn.
- Improve smoothness and luster of yarn.
- Produce much clear yarn.
- Improve the efficiency of the next process.
- Reduce the hairiness of the yarn.
- Improve better twist distribution in the yarn.
Major Manufacturers of Comber:
- Marzoli Spa, Italy
- Laxmi Machine Works Limited
- Toyoda Textile Machinery, Japan
- Rieter Machine Works Limited, Switzerland
- Zhejiang Huahai Group, China
- Jinwei Textile Machinery, Co. Limited.
Hook Fiber:
The undesirable bending of the fiber ends produces fiber hook. It is the disadvantages of web formation at the card. According to an investigation by Morton & Yen in Manchester, the fibers in the web:
- More then 50% have trailing hook
- About 15% have leading hook
- About 15% have double hook
- And less than 20% of the fiber have no hook.
Hook fibers effectively convert longer fiber to short fibers and these cannot be permitted in the yarn. They must therefore be removed before yarn formation. This can be done either by drafting at draw frame or combing at comber.
Required no. of Machine Passages:
The comber mainly straightens out the leading hooks. That’s why leading hook must be presented to the comber. Reversal of the hook occurs at each processing stage between the card and drawing I, drawing II and comber. Therefore, definite number of machine passages is required in intervening stages. Between the card and comber there must be an even number of passages, and an odd number between the card and ring spinning machine. In rotor spinning machine, the disposition of hooks is of little significance.
Preparation of Raw Materials for Comber:
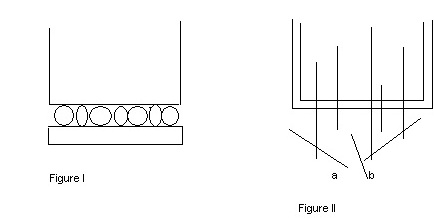
The raw materials delivered by the carding machine are not suitable for combing both as regards form and fiber arrangement. If card sliver were feed to the comber, then true nipping by the nipping plates (Figure I) could occur only on the high points, with the risk that the nippers could not retain the less strongly compressed edge zone of the slivers. These could be pulled out as clumps by the cylinder combs. That’s why a sheet with greatest possible degree of evenness is therefore required as in feed to the comber.
A good parallel disposition of fibers within the sheet is a further prerequisite. If the fiber lies across the strand (a in fig. II), even long fibers are presented to cylinder combs as if they were short fibers (as shown in b) and they are eliminated as such. This represents unnecessary loss of good fibers.
Types of Comber:
There are different types of combers are available. These are given below:
- Rectilinear Comber (with stationery or oscillating nipper)
- Circular comber
- Rotary comber
- Hackling machine (bast fibers)
Passage Diagram of a Comber Machine:
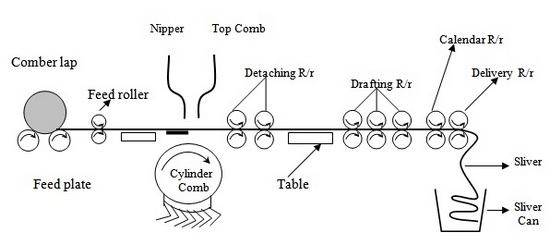
Basic Principle of a Comber (Combing sequence/ cycle):
One article has written about basic principle of a comber. So here only title of comber principle is given below.
- Lap feeding by feed roller
- Lap nipping by the nipper
- Combing by the cylinder
- Nipper opening and forwarding
- Detaching roller backward movement
- Piecing
- Combing by the top comb
- Detaching roller forward movement
- Starting a new cycle
- Cleaning of cylinder comb
Advantages of Combing Process:
Combing provides multiple advantages in subsequent processing steps that are Summarized below:
1. Purpose of combing process:
- Removal of short fibers
- Fibers parallelization
- Removal of contaminants
2. Advantages of the combed sliver:
- Improvement of the histogram
- Parallel, straightened fibers
- Very low dirt content
3. Advantages during spinning and in the yarn:
Compared to uncombed cotton,
- Yarn tenacity is higher
- Yarns of finer titer can be spun
- Higher production speeds are possible
- Yarn twist can be reduced
- Less yarn breaks occur during spinning
- Less fiber fly is released during spinning
4. Advantages during weaving, knitting preparation:
Higher efficiency in comparison to yarns of uncombed cotton is caused by
- Less yarn breaks
- Less abrasion (less yarn friction)
- Less fiber fly
5. Advantages during weaving/knitting:
During weaving and knitting, combing provides
- Higher tenacity of the woven or knitted fabrics
- Less contamination
- Higher bursting strength
- Better luster
- Less hairiness
- Softer handle
Faults in Combing Process:
a) Cutting across:
Thick and thin places across the width of the web.
Causes:
- The fault originates in the laps owing to the use of incorrect setting, excessive draft at the lap former.
- Incorrect timing of the detaching roller.
- Top comb setting too deeply.
b) Curling:
The term is applied when a group of fibers curls as they leave detaching roller.
Causes:
- Faulty detaching roller covering.
- Dirt in the top detaching rollers.
- Excessive brush speed.
- Bent needle of cylinder and top comb.
c) Cotton not combing at one head:
Causes:
- Pawl not gearing properly with feed ratchet wheel.
- Foreign matter wedge between nipper and feed plate.
- Damaged part of cylinder and top comb.
d) Detaching roller lapping:
Causes:
- Incorrect atmospheric condition.
- Oil on rollers
- Sticky matter or dirt on rollers
- Worn out roller coating.
- Bad top cleaners.
e) Irregular sliver:
Causes:
- Excessive tension on calendar roller.
- Improper roller setting.
- Faulty adjustment of suction unit.
- Eccentricity of roller.
Published By
S. M. Hossen Uzzal
B.Sc. in Textile Technology
Monno Fabrics Ltd. Manikgonj.
Email: smhossen.tex@gmail.com
You may also like:
- Comber Machine Production Calculation
- List of Spinning Machines with Manufacturers Name
- Recent Development of Carding Machine in Yarn Spinning
